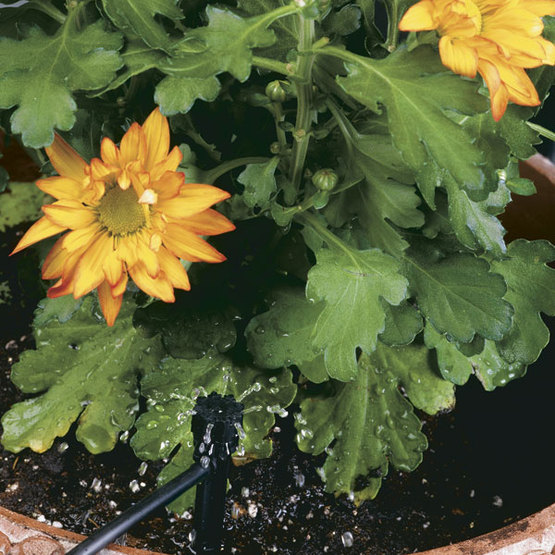

When my wife and I planted ornamental gardens in Sandy, Utah, we knew we’d have to somehow irrigate our plants. For several years, we watered with a hose and sprinkler, but that got old in a hurry. We considered in-ground sprinkler systems, but they seemed costly and wasteful of water. Then I learned about the merits of drip irrigation. With a series of carefully placed emitters, water could be delivered right to the root zones of plants. And we could enjoy the convenience of a permanent watering system. Water is a finite natural resource. As populations increase in North America, many areas are facing water shortages and periodic droughts. These crises make a water-thrifty garden irrigation system an attractive tool. With a drip system, my plants thrive with less water. Keeping water off foliage also cuts down on fungal diseases. When I occasionally use pesticides, they aren’t washed off when the system kicks in. And, since only the roots of plants that I want get watered, many fewer weeds pop up. With a simple drip-irrigation system, you can water perennials, annuals, shrubs, trees, ground covers, and even potted plants.
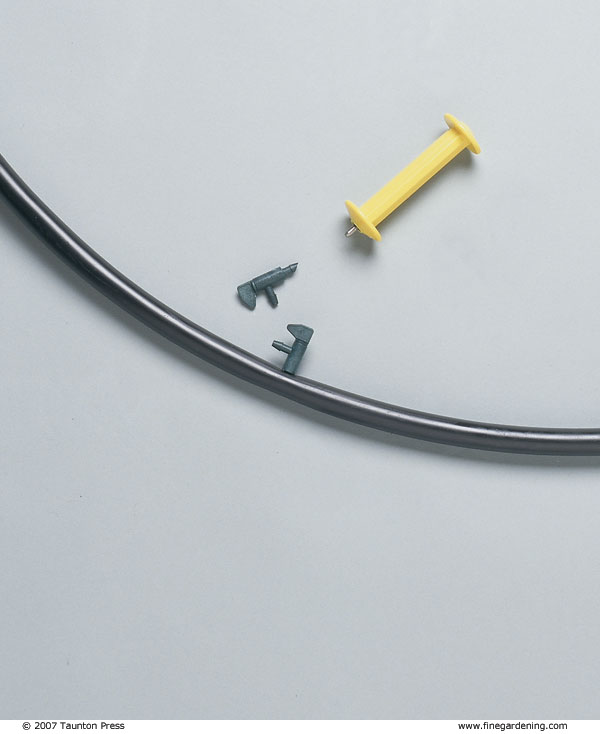
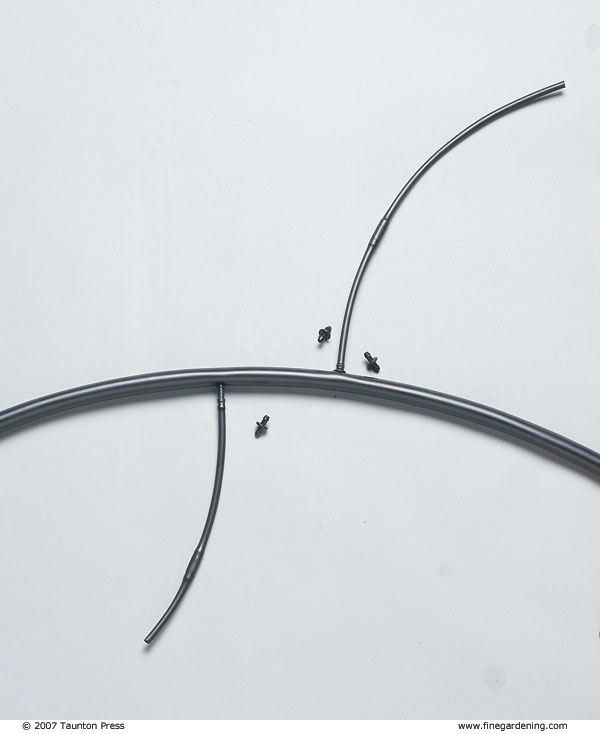
Flexible parts snap together
Think of a drip irrigation system as an upscale soaker hose. But instead of water spraying out every 2 inches, it can seep out every foot—or maybe every 3 feet—drip by drip. With a little planning, those drips can line up with the root zones of plants.
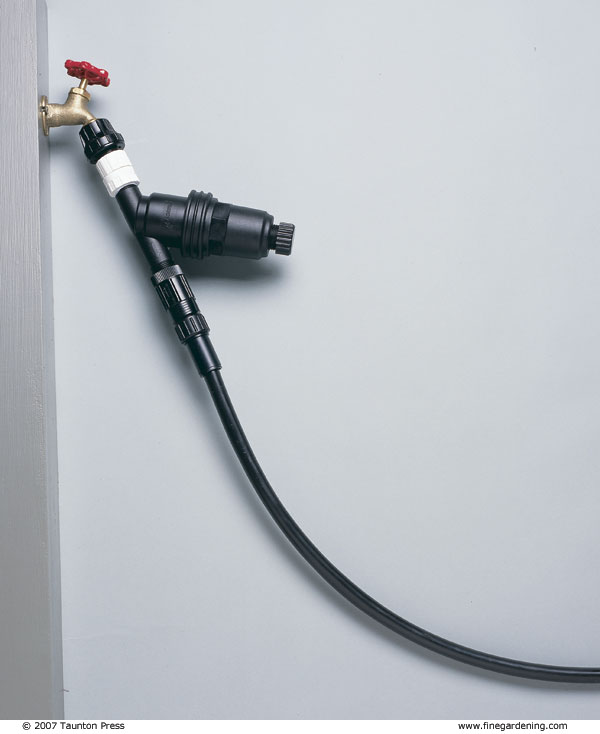
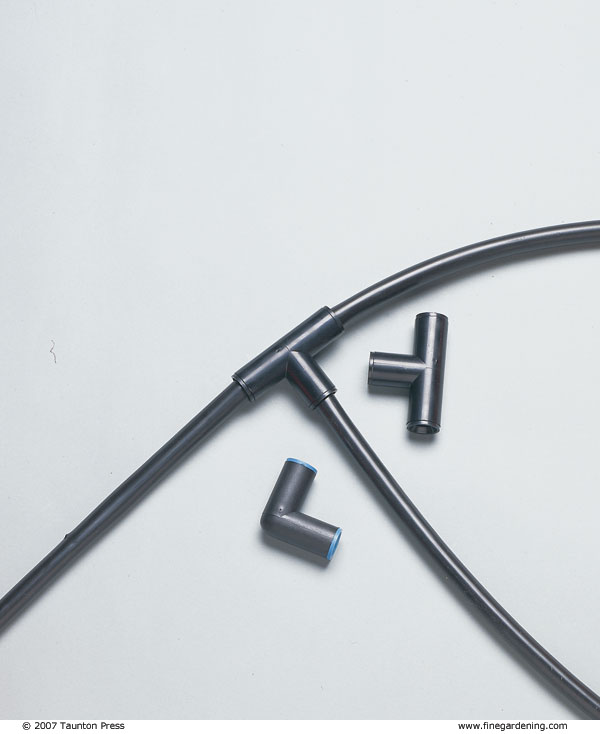
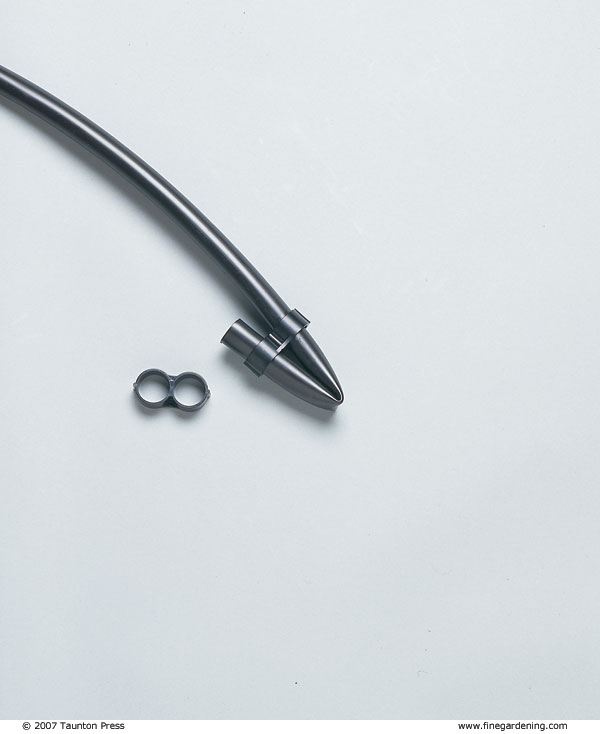
Drip-irrigation parts snap together like modular toys and can be adjusted as your garden changes. You’ll need a filter, water-pressure reducer, hose swivels, emitters, and 1/2- or 5/8-inch flexible polyethylene tubing—also called the submain. You may need a backflow preventer if it’s required by your municipal water department. Optional parts include 1/4-inch solid tubing, 1/4-inch drip line, connecting tees, 90-degree elbows, connecting barbs, hold-downs to keep tubing in place, goof plugs to fill holes you decide not to use, timers, and fertilizer injectors. You can buy these parts at some hardware stores or garden centers, or from companies specializing in irrigation systems. Parts from different manufacturers are almost always interchangeable.
System costs are very reasonable. You could cover about 250 square feet with drip irrigation for $20 to $50 in parts, not including a timer. For installation, all you need are strong shears to cut the tubing, and a 16-penny nail or commercial punch to poke holes in the submain for the emitters and 1/4-inch tubing. You can bury the submain just below the soil, or leave it on the surface and cover it with mulch. Either way, I try to run it along the edge of a bed so I won’t accidentally disturb it. The 1/4-inch tubing can also be buried, but leave drip lines on the surface so the emitters don’t clog with soil. I use a combination of buried and mulched lines in my garden, so only small emitters are visible here and there.
You can convert an existing sprinkler system to drip irrigation by plugging all the spray heads on a circuit but one, and running a drip circuit from that one head. Remember to choose circuits that aren’t needed to water the lawn.
There are two critical points to keep in mind. First, drip irrigation works on low pressure—from 10 to 30 pounds per square inch (psi). However, water pressure at hose spigots runs anywhere from 50 to 100 psi so you need a pressure reducer on every drip-irrigation circuit. Second, as a conservative rule of thumb, any one drip-irrigation circuit can only handle about 225 gallons per hour, so you’ll need to calculate the total gph for all emitters on each drip circuit to make sure they don’t exceed this amount. Each emitter has its own rating, so simply add up the numbers.





Assess your watering needs and map out a system
Use a tape measure to roughly determine how much flexible tubing you’ll need for the submain. Start at the hose spigot and work your way through your garden. The total run of submain on any one drip-irrigation circuit should not exceed 400 feet. While the tubing is flexible, for a 90-degree turn you’ll need an elbow. If you want to branch the submain, use a connecting tee.
Wherever the submain runs within a few inches of a plant, you can snap in an emitter to provide water. The emitter has a connecting barb on one end. To water a plant further from the submain, put a barb in the submain, attach 1/4-inch solid tubing to the barb, then put an emitter on the other end.
Figuring how many emitters you’ll need is not a hard-and-fast proposition. You’ll have to consider your soil type, the plants’ sizes and general water needs, your garden’s microclimates, and whether you use mulch. A 1-gph emitter will cover an area 12 inches in diameter in sandy soil or an area 18 inches in diameter in clay soil. I generally give 1-gallon-size plants a single 1-gph emitter right on the root ball. With larger plants, I start with one 1-gph emitter per foot of branch-spread diameter. Got a 4-foot-diameter bush? Space four 1-gph emitters halfway between the trunk and the drip line. I use 1-gph emitters because it’s easier to keep track of how many gph are on any given line.
For perennial or annual beds, I use 1/4-inch drip-line tubing with built-in 1/2-gph emitters every 12 inches. This tubing attaches to the submain with a connecting barb; each line can snake up to 50 feet through a bed. Drip lines work best with a 25-psi pressure reducer.
To get the equivalent of an inch of rainwater from a 1-gph emitter takes just shy of an hour. In our hot Utah climate, 2 inches of water per week is recommended during the growing season. Consult a county extension agent for the recommendation in your area.
Individual plants are the best indicators of how long you need to water. If plants look the worse for wear at 5 p.m. on a hot, sunny day, that’s pretty common. But if the same plants still look wilted early the next morning, you need to investigate. You can check soil moisture with an old screwdriver. In damp soil, it’s easy to push in the screwdriver. In dry soil, you’ll need help from a big hammer. If the soil is dry, then your plants aren’t getting enough water. Run the system longer each time, or add more emitters. If the soil is wet, then you might be overwatering. Pay special attention to new plants because their roots haven’t spread out in the soil yet. Just because the soil is damp a few inches from a new plant doesn’t mean the plant is getting any water.
It’s best to water deeply but infrequently. If there are puddles by emitters, you’ve run your system too long. Instead, you should see a small area of damp earth. Below the surface, where roots can go as deep as 18 inches, water will spread out and sink into the soil.
Overwinter your system
Maintenance for a drip system is fairly simple. If you live where it freezes in winter, disconnect the line from the spigot in the fall and take the backflow preventer, pressure reducer, and filter inside. The other tubing is flexible and should not split when frozen. Tie plastic wrap over the end of the submain. In spring, open the end of the submain, and flush the system to get rid of debris. In a warm climate, your entire system may remain in place year-round.
I’ve used drip irrigation for 6 years now and everything from petunias to pine trees is doing just fine, thank you. And, as a bonus, my water bills are lower than most of my neighbors’.

















Comments
I couldn't find a date on this article. I read it in November of 2020. Quite a bit of the information is not current; from drip parts to where feeder roots are located. I'm new to FG. Maybe that's it.
Log in or create an account to post a comment.
Sign up Log in